Diabetic Retinopathy

Diabetic retinopathy is an eye condition that can cause severe vision loss if left untreated. At the Eye Center of St. Augustine, our eye doctors specialize in diagnosing diabetic retinopathy and are dedicated to ensuring that you get the treatment you need to preserve your vision.
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic is a common eye condition that occurs as a complication of diabetes. Often, diabetic retinopathy develops as a result of consistently uncontrolled blood sugar levels.
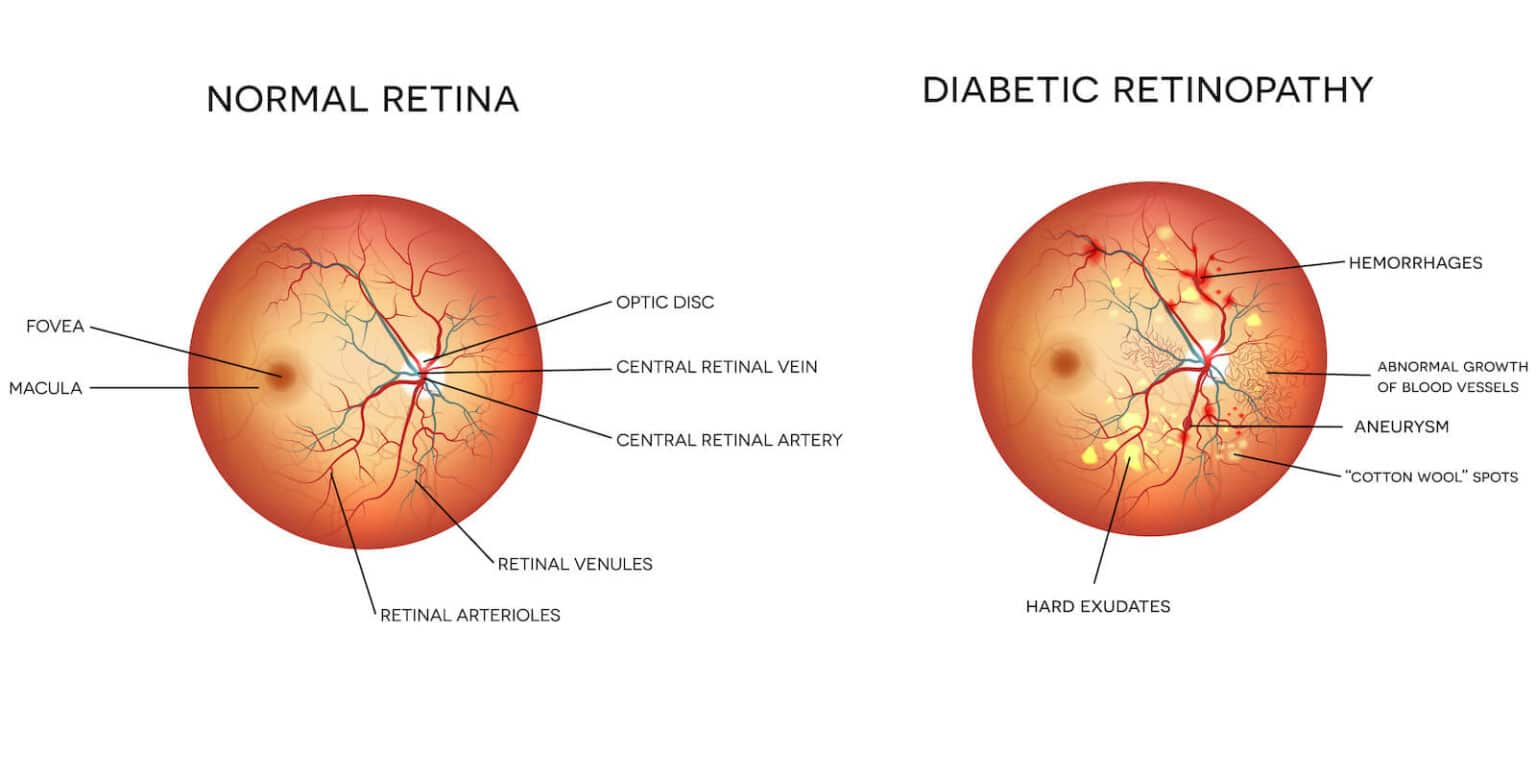
The eye condition causes damage to the blood vessels in the retina, which is located at the back of the eye. The healthy functioning of the retina is vital for you to experience clear vision.
The retina is a light-sensitive tissue that gathers information from light and sends it to the brain to be processed into an image. Elevated blood sugar levels can cause blockages in the blood vessels that nourish the retina.
When these blood vessels become damaged, your eye will attempt to compensate for these damaged blood vessels by growing new blood vessels. However, these new blood vessels are irregular and poorly formed.
Because they are formed poorly, they are delicate and can leak easily break and leak. Careful management of your diabetes, including control of your blood sugar levels, can prevent you from developing diabetic retinopathy and experiencing vision loss.
There are two main types of diabetic retinopathy: non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy, also known as NPDR, and proliferative diabetic retinopathy, also known as PDR. NPDR is the most common form of the eye condition and is also less severe.
NPDR is often the beginning stage of diabetic retinopathy and is characterized by the blockage of blood vessels. PDR is a more advanced form of diabetic retinopathy and is characterized by the formation of new blood vessels.
If the condition reaches this stage, your risk for more severe permanent vision loss is increased.
What Are the Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy?
In the early stages of diabetic retinopathy, you may not notice very many symptoms. However, as the condition worsens, you may notice some of these symptoms:
In most cases, symptoms of diabetic retinopathy appear in both eyes. If you have diabetes and are experiencing any of these symptoms, schedule an appointment with your eye doctor right away.
How Do Eye Doctors at The Eye Center of St. Augustine Detect Diabetic Retinopathy?
If you have diabetes, your primary care physician or endocrinologist will likely recommend you regularly visit your eye doctor for diabetic eye disease screening. Your eye doctor can diagnose diabetic retinopathy during a comprehensive eye exam.
In order to view the retina, your eye doctor will place dilation drops into your eyes. Dilation drops will widen your pupil and allow your eye doctor to view your retina at the back of your eye with a special microscope.
If your eye doctor detects signs of diabetic retinopathy during their examination of your eyes, they may conduct further testing. Optical coherence tomography, or OCT, is a type of test that takes detailed images of your retina.
Additional tests can help your eye doctor diagnose diabetic retinopathy and determine the severity of the eye condition in each case. At the Eye Center of St. Augustine, we regularly perform diabetic retinopathy screenings to ensure that our patients aren’t at risk for vision loss.
Do you have diabetes, but it’s been a while since your last eye exam? Schedule an appointment at the Eye Center of St. Augustine in St. Augustine, FL, today to ensure you are not at risk for developing diabetic retinopathy!
